ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces:3D打印三维分级多孔非晶复合催化剂及其高效降解废水性能
杨冲,张诚,柳林
Abstract: Finding highly efficient and reusable catalysts for advanced oxidation processes is a crucial endeavor to resolve the severe water pollution problems. Although numerous nanocatalysts have been developed in the past few decades, their recyclability along with sustainably high catalytic efficiency still remain challenging. Here, we propose a new strategy for designing efficient and reusable catalysts, that is, introducing Cu as a reductant into a metallic glass-based catalyst and constructing three-dimensional hierarchical porous architectures via a laser 3D printing technique. The as-printed 3D porous MG/Cu catalysts exhibit exceptional catalytic efficiency in degrading RhB with a normalized rate constant approximately 620 times higher than commercial nano zero-valent iron, outperforming most reported Fenton-type catalysts so far. Strikingly, the catalysts exhibit an excellent reusability and can be used more than 100 times (the highest record so far) without apparent efficiency decay. It is revealed that Cu-doping could improve the surface reducibility and promote the electronic transfer, rendering the 3D-printed MG/Cu catalysts with a sustainably active Fe(II)-rich surface and, therefore, unprecedented reusability. This work offers a broadly applicable design route for the development of advanced catalysts with an outstanding combination of activity and reusability for wastewater treatments.
文章导读:
高级氧化(Advanced oxidation processes, AOP)是工业界最常用的废水处理技术之一,而开发高效、高稳定性的催化剂是当前AOP技术发展与应用的关键。近几十年来,虽然各种纳米催化剂(如纳米零价铁、Fe2O3、FeOCl)相继被开发处理,但是这些纳米颗粒状催化剂的循环使用次数极其有限(通常小于10次),分离困难,限制了其工业应用。与晶态催化剂相比,非晶合金催化剂通常表现出更高的活性和循环性能。但非晶合金催化剂形态因制备技术限制,通常局限于条带状,其较小的比表面积不利于催化反应。
最近,华中科技大学非晶态材料研究实验室柳林课题组通过在非晶合金中原位引入还原性Cu,并采用激光3D打印技术成功制备了三维分级多孔Fe基非晶合金/Cu复合催化剂(3DP MG/Cu),并系统研究了其降解废水性能。所开发的新型3DP MG/Cu催化剂对罗丹明B染料表现出极高的催化降解活性,其约化反应速率常数比商用纳米零价铁催化剂高出了近620倍。与此同时,3DP MG/Cu催化剂还表现出优异的循环稳定性,在循环使用100次后,其降解效率仍未显著降低。研究发现:原位引入Cu相可以提高非晶合金催化剂表面的还原性,同时加快电子传输速率,使得3DP MG/Cu催化剂表面长期富集高活性的Fe(II)物种,从而导致高活性和优异的循环性能。此外,作者们还利用该技术进一步制备了大尺寸栅格状非晶合金复合催化剂,验证了其连续动态降解废水性能。发现流动的废水可以在短时间内快速降解,表明该催化剂具有良好的工业应用前景。
相关工作发表在ACS Applied Materials & Interface 13 (2021) 7227-7237上。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金重点项目与面上基金(51531003, 51771077)、湖北省重点研发计划(2020BAB075)和湖北省杰青项目(2020CFA086)资助。
文章链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.0c20832?ref=pdf
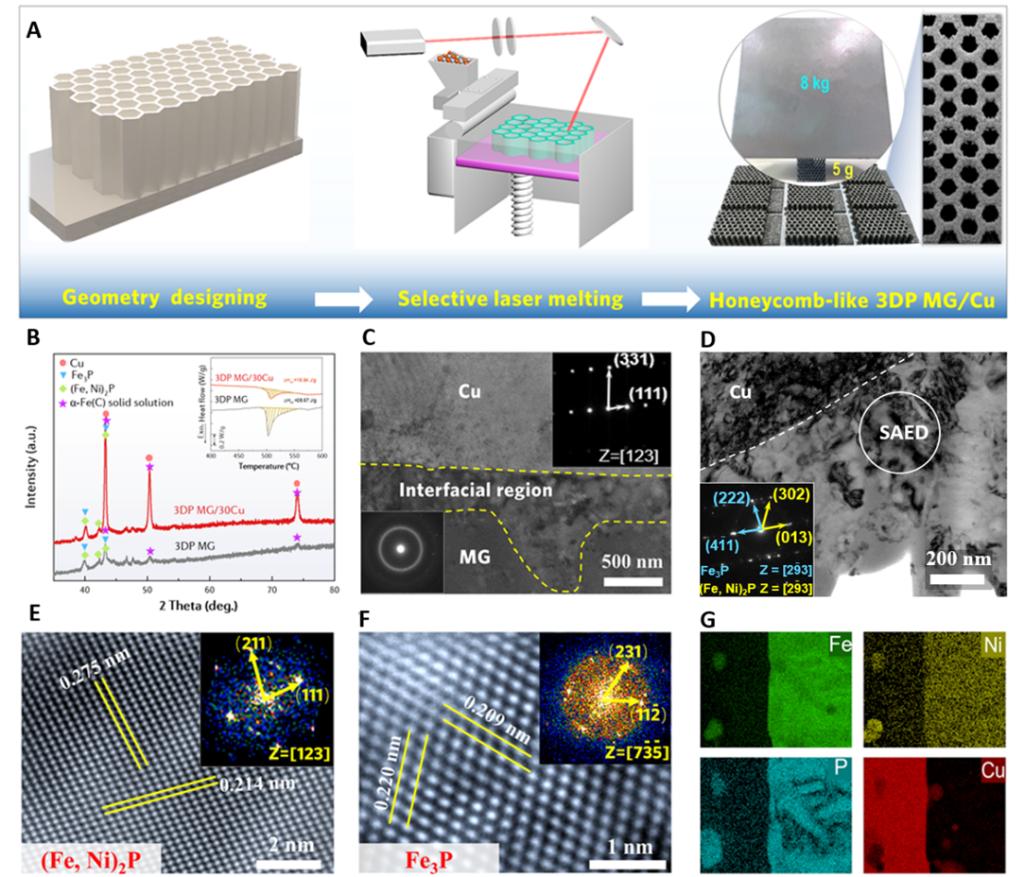
图1 3D打印非晶合金/Cu复合催化剂结构表征
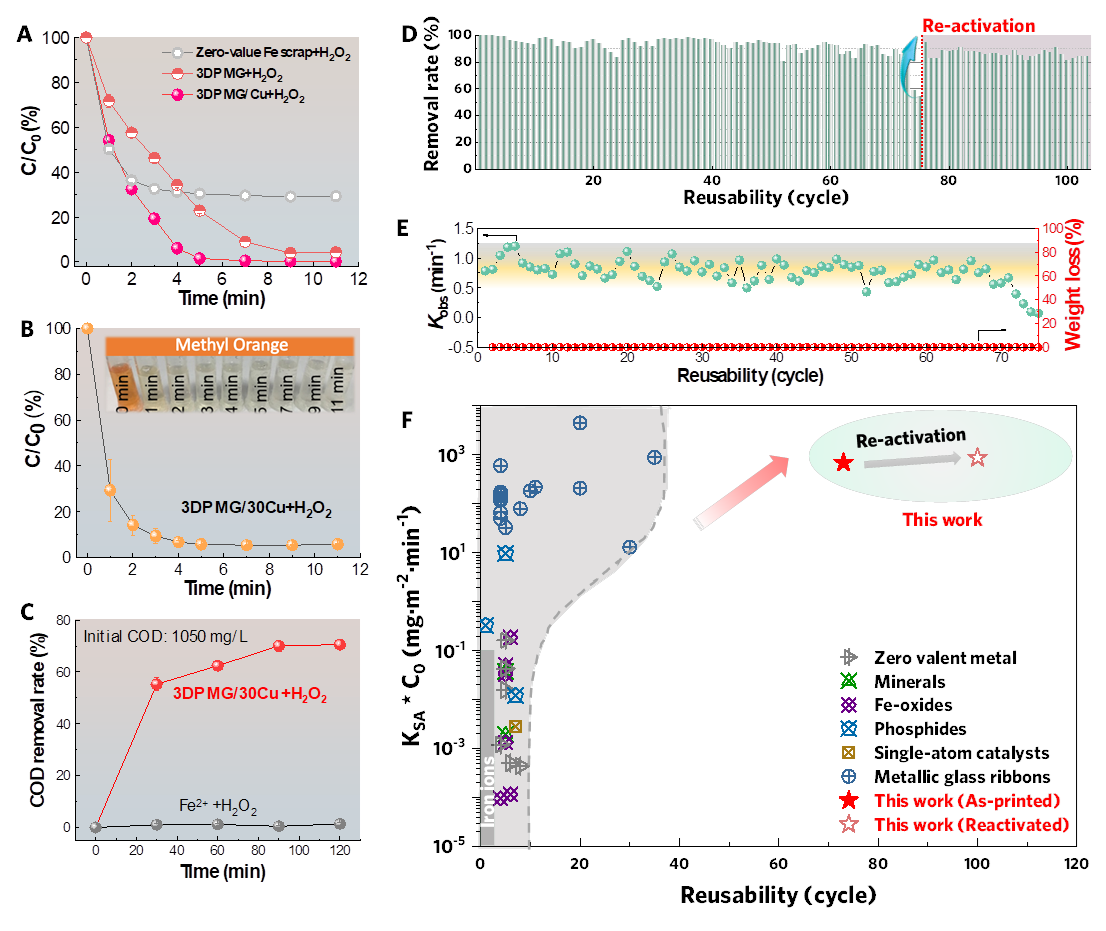
图2 3D打印非晶合金/Cu复合材料催化降解染料废水性能
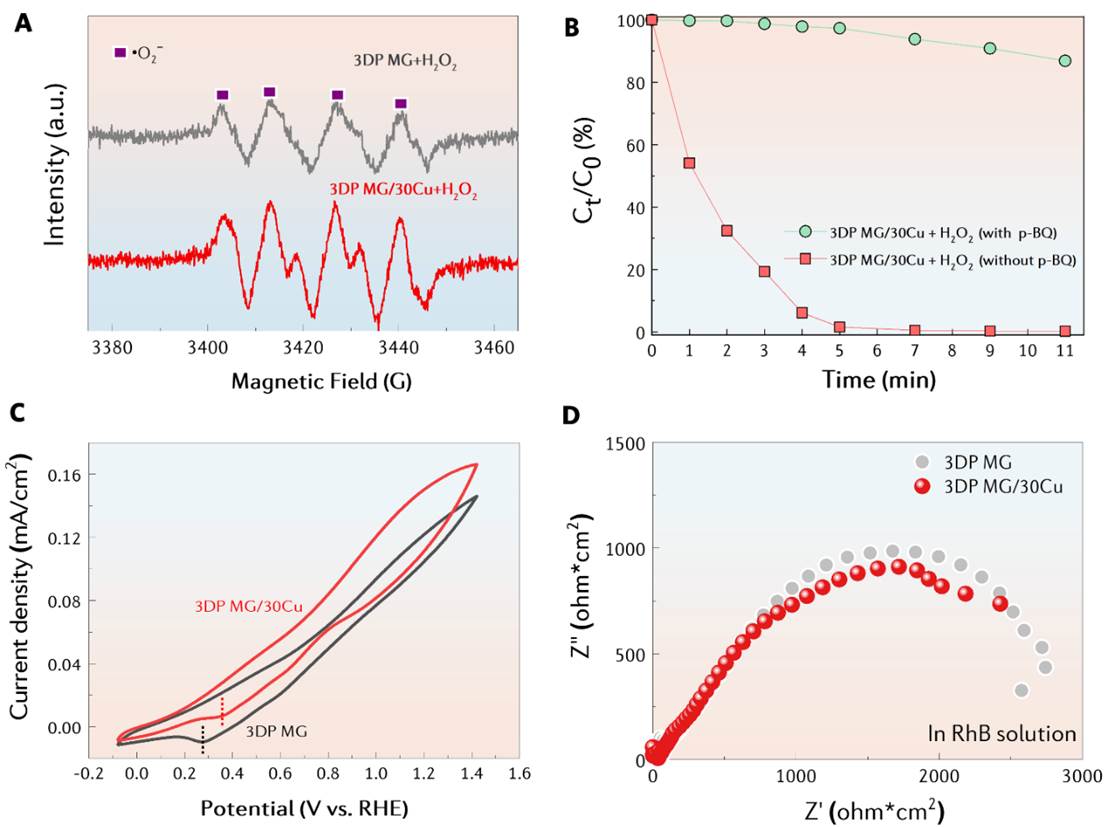
图3 3D打印非晶合金/Cu复合材料催化降解废水机制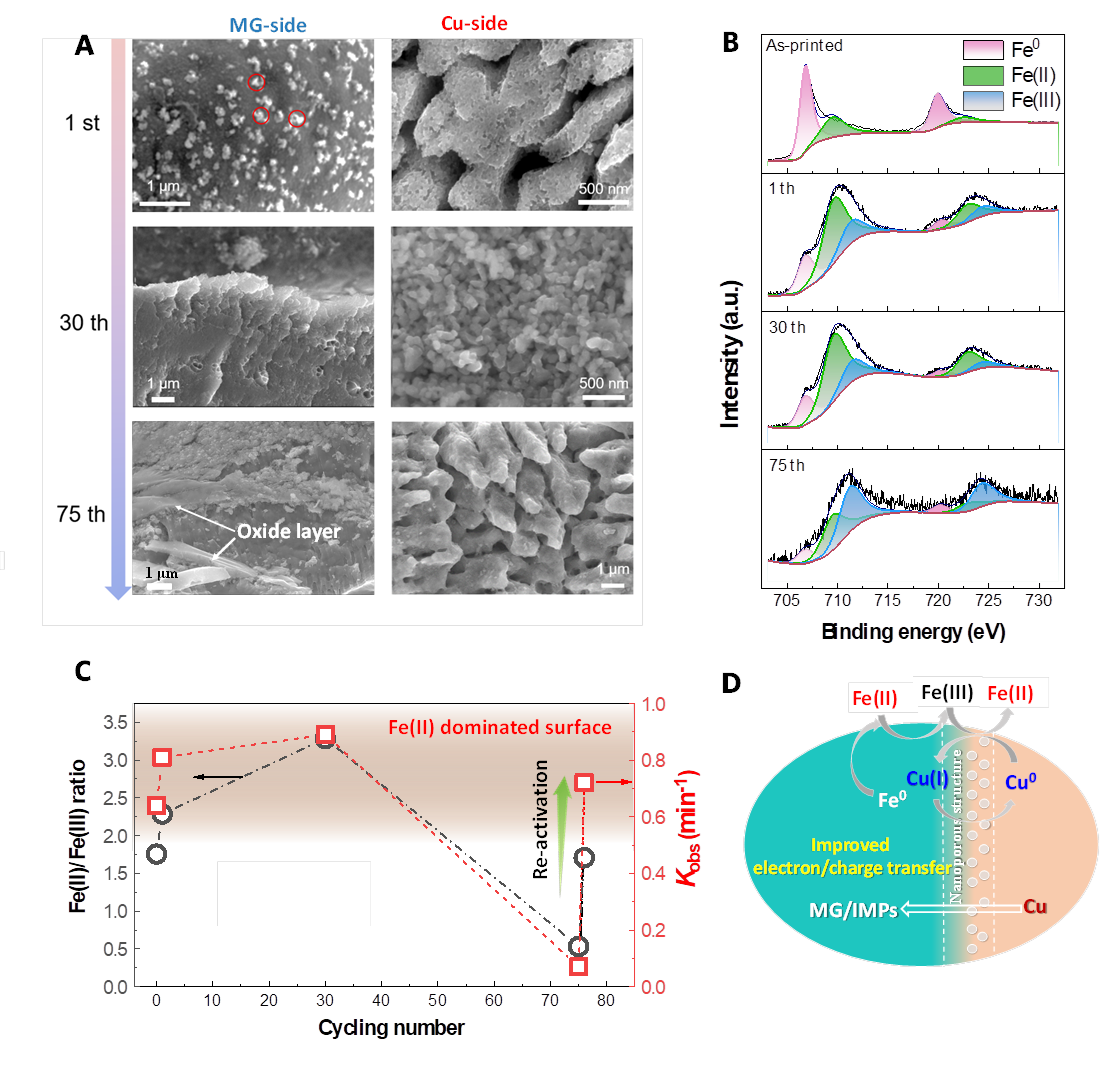
图4 3D打印非晶合金/Cu复合材料不同循环次数后结构表征及反应机制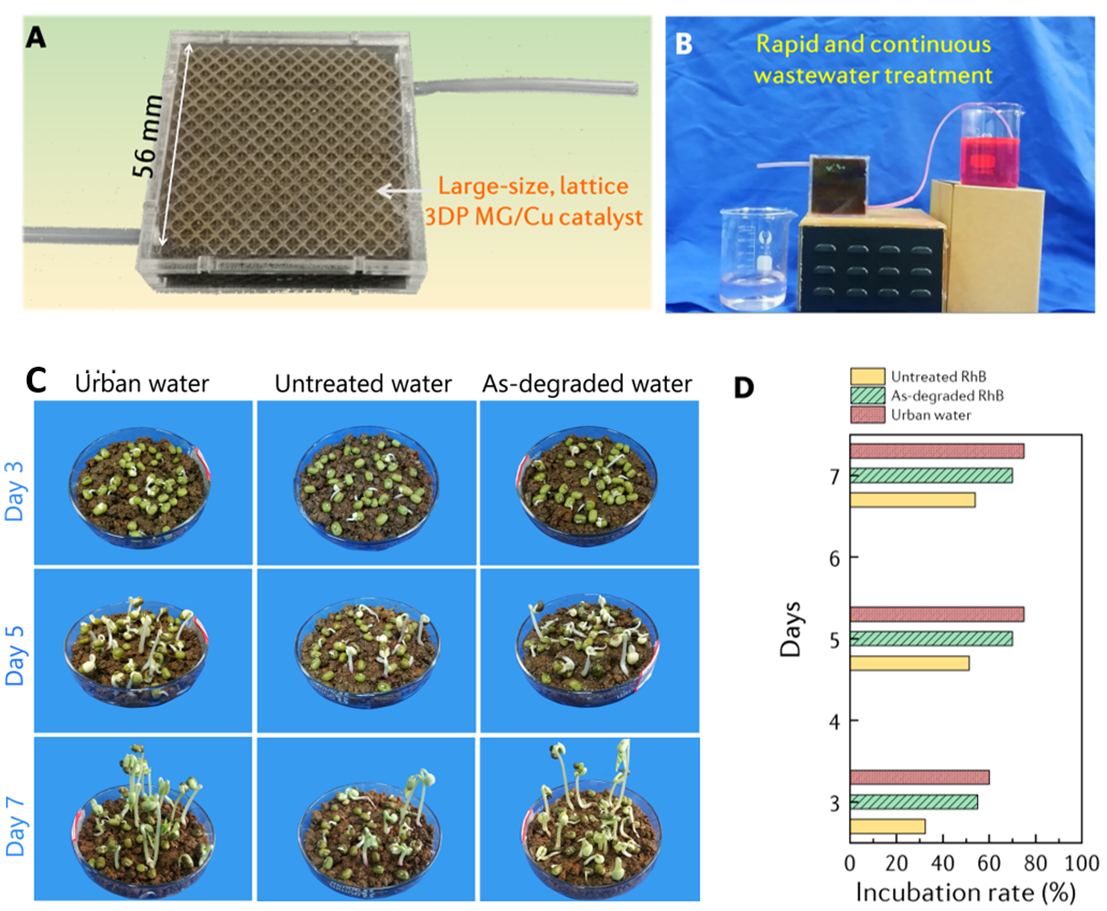
图5 3D打印非晶合金/Cu复合催化剂(网格状)动态降解流动废水性能及处理后水质的毒性评价