Authors: Sudip Kumar Lahiri, Cheng Zhang, Mika Sillanpää, Lin Liu*
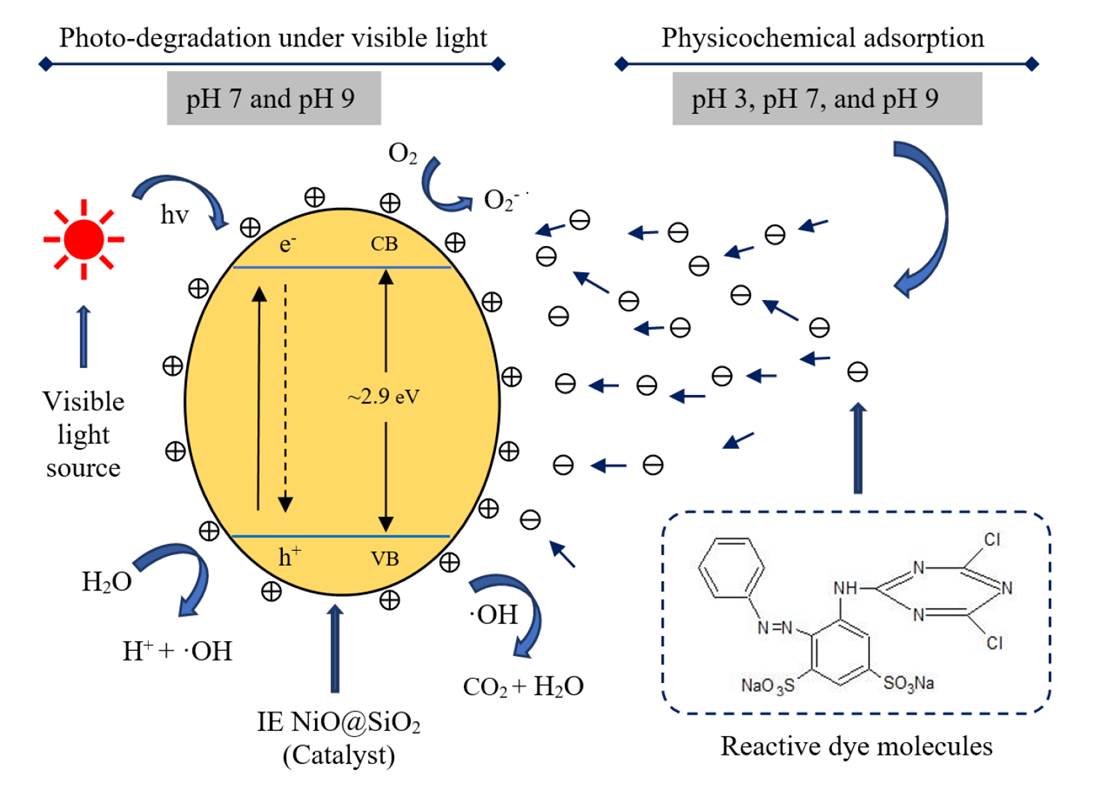
Photo-catalytic elimination of organic contaminants plays a significant role in wastewater treatment. Developing a highly efficient photo-catalyst is one of the leading research topics. Herein, we reported the fabrication of a novel nanoporous NiO@SiO2 photo-catalyst by a simple ion-exchange method to eliminate the reactive dyes. The synthesized NiO@SiO2 catalyst exhibited fast photo-degradation and excellent adsorption capability and could efficiently remove Red-FN-3GL dye from wastewater, due to a high loading of NiO and a large specific surface area, abundant electron-withdrawing groups as well as narrow bandgap energy. In addition, the NiO@SiO2 photo-catalyst also displayed a high capability to remove reactive dyes over a wide range of pH values (pH 3-9). The prominent adsorption and photo-degradation of dyes were strongly dependent on the surface charge of the catalyst and the generation of hydroxyl radicals (OH•) by the catalyst, respectively. Furthermore, the NiO@SiO2 photo-catalyst also exhibited excellent recyclability, thus demonstrating the feasibility of practical applications in industries. The strategy of covering the metal-oxide to nanoporous silica is a promising method for developing active photo-catalysts and applying them in the wastewater treatments.