Journal of Materials Science & Technology: 通过双纳米沉淀和晶界偏析实现了激光粉末床熔合AlFeCuZr合金的高强度
第一作者:徐京豫 通讯作者:张诚,柳林
Abstract:
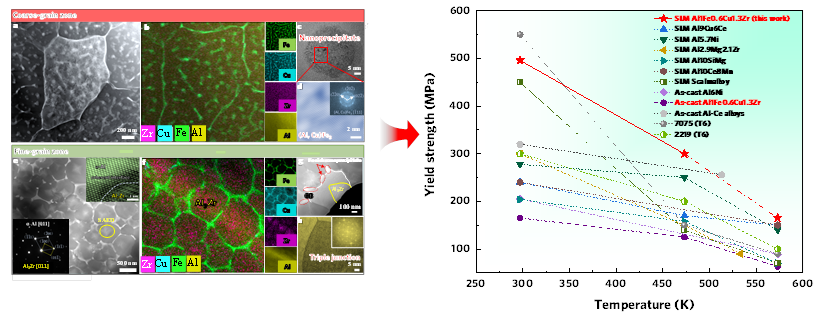
Additive manufacturing of aluminum alloys has received significant attention in the aerospace industry; however, achieving sufficient high strength, especially at elevated temperatures, remains challenging. Here, a crack-free and near-full dense Al-1Fe-0.6Cu-1.3Zr alloy was fabricated by the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technique. The Al-Fe-Cu-Zr alloy exhibits heterogeneous microstructures with two distinct zones. One is the so-called coarse-grain zones (CGZs) with an average grain size of 0.95 μm, where (Al, Cu)Fe3 nanoparticles precipitate in the Al matrix and Fe and Cu cosegregate at the grain boundaries (GBs). The other is fine-grain zones (FGZs) with an average grain size of 0.45 μm, where an Al3Zr nanoparticle precipitates in each of the a-Al grains (serves as the nuclei), and Fe-rich nanoprecipitates and Fe/Cu cosegregation appear at the GBs. As a result, the LPBF Al-Fe-Cu-Zr alloy, with these unique heterogeneous structures, displays high strength at both room temperature and elevated temperatures, e.g., with high yield strengths of 500 MPa at room temperature, and 163 MPa at 573 K, both are higher than those of additive manufactured Al-based alloys reported thus far. It is suggested that the high strength over a wide temperature range of the current LPBF Al alloy is mainly attributed to the combination of the precipitation strengthening mechanism and grain-boundary strengthening mechanism
文章导读:
铝合金因重量轻、比强度高而被广泛应用于航空航天和汽车工业。然而,通过传统工艺制造具有复杂几何形状的铝合金部件面临严峻的挑战。为了解决这个问题,激光粉末床熔合(LPBF),近年来已被应用于制造形状复杂的铝合金部件,这是其他方法难以实现的。因为可加工性差和容易氧化,LPBF 制造铝合金具有挑战性。迄今为止,只有少数铝合金体系可以通过 LPBF 可靠制造,其中大多数是近共晶 Al-Si-(Mg) 合金。LPBF Al-Si-Mg 合金的强度没有竞争力,在室温下通常小于 250 MPa,并且在高温下迅速下降。例如,屈服强度在 573 K 时降低到 80 MPa,使这种合金在高温环境中不能使用。另一方面,传统的时效硬化高强度铝合金,如 2xxx (Al-Cu-Mg)、6xxx (Al-Mg-Si) 和 7xxx (Al-Zn-Mg) 系,几乎不能通过LPBF 制备,因为它们会因高热应力开裂。因此,迫切需要设计在室温和高温下均具有良好机械性能并可通过 LPBF 制造的新型铝合金。
最近,华中科技大学非晶态材料研究实验室柳林课题组开发了一种新型无裂纹且近乎全致密的LPBF-AlFeCuZr合金,具有优异的室温和高温强度。制备的 AlFeCuZr 合金呈现出具有两个不同区域的异质微观结构:一个由细晶粒组成,而另一个由粗晶粒组成。在粗晶区, (Al, Cu)Fe3 纳米粒子在晶粒内部析出, 而 Fe 和 Cu 在晶界处共分离。在细晶粒区,Al3Zr 颗粒在每个晶粒内析出,而 Fe 和 Cu 共同偏聚以及纳米富铁析出相在晶界处形成。LPBF制备的AlFeCuZr合金的屈服强度在室温下达到了500 MPa,在 573 K下达到了163 MPa,超过大多数传统的 LPBF 铝合金。如此好的高温强度归因于双纳米析出强化和晶界强化。这项工作展示了一种有效利用 LPBF制造的铝合金中的共晶结构和析出强化效应新型的微观结构设计策略。
相关工作近期发表在期刊Journal of Materials Science & Technology上,研究得到了国家自然科学基金(No. 52061160483 和 92166130)和湖北省杰出青年科学基金(No.2020CFA086)的资助。